Scientists estimate that the human body may contain as many as 400,000 proteins. During the last year, biomedical research has mainly focused on SARS-CoV-2 virus establishing that it is composed by 26 proteins including the Spike protein. This protein is the carrier that allows the virus to entry our body.
Spike protein structure and its action on human body have been studied trough cryo-electronic microscopy (Nobel Prize in Chemistry 2017). Protein samples are rapidly frozen at very low temperatures in order to avoid ice crystals formation and to observe their usual structure.
An electron microscope repeatedly emits a beam of electrons through the sample, producing a series of two-dimensional images from different angles. A combination of two-dimensional images creates a three-dimensional image of the protein.
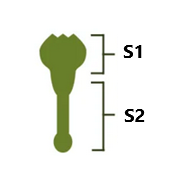
Spike protein is composed of two subunits:
- S1 subunit forms the upper part of the protein. Its function is to bind to the ACE2 receptor, which is present in many cell types, including organs. The ACE2 is an enzyme produced by the endothelial cells of blood vessels that supply all organs, especially lungs. It controls the Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone system.
- S2 subunit composes the lower part of the protein and is responsible for cellular membrane fusion. This is what allows the virus to enter human body.
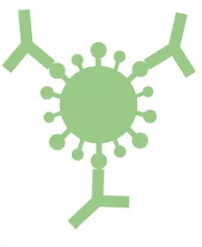
Spike protein is made up of three individual proteins: each viral particle contains approximately 26 of these trimers. Each trimer is sprinkled with sugar molecules, glycans (polysaccharides constituting glycolipids and cell membrane glycoproteins), which coat the Spike protein, camouflaging it from our immune system.
Knowing the structure of the Spike protein has been very useful in the fight against the virus: it has hastened the development of vaccines, many of which are based around this protein, it has made us understand how the virus infiltrate and acts in our body helping the research of potential medicines to fight it. It also helped scientists understand how our antibodies try to neutralize the virus – that is how genetic mutations might affect it. Some of these mutations can introduce changes in the structure of the Spike protein, so being able to compare the structures between different variants of the virus helps us understand how these changes might affect it.
ACTIVITY: Some time after the start of the pandemic, what reflections can you make on the social and economic consequences that have occurred? Write a short text.